Enabling Fleet Desktop on Fedora, Debian, and openSUSE
{{articleSubtitle}}
Lucas Rodriguez
Enabling Fleet Desktop on Fedora, Debian, and openSUSE
{{articleSubtitle}}
Lucas Rodriguez
Enabling Fleet Desktop on Fedora, Debian, and openSUSE
Fleet Desktop is a menu bar icon for macOS, Linux, and Windows that gives end users visibility into how their device is managed by Fleet and functions as a self-service portal.
On Linux systems, Fleet Desktop appears as an icon in the menu bar. Fedora and Debian do not support tray icons by default and rely on the appindicator-support GNOME extension for enabling tray icons. GNOME extensions prompt the end user to accept the installation.
This article explains how admins can enable Fleet Desktop on Linux by using policy queries paired with script execution.
Policy and script execution
The policy query defined in check-fleet-desktop-extension-enabled.yml (from our Dogfood environment) checks if the extension needed for Fleet Desktop is installed and enabled on Fedora, Debian, and openSUSE hosts.
NOTE: fleetd 1.41.0 is required (the policy query relies on a table added to that version).
Starting in version v4.58.0, Fleet supports running scripts to remediate failing policies (see the Automatically run scripts article for more information). Admins can therefore configure Fleet to run install-fleet-desktop-required-extension.sh on devices where the policy detects the extension is missing (check-fleet-desktop-extension-enabled.yml contains both the policy and remediation script).
End-user experience
The screenshots below show the end-user experience when Fleet runs the script to install the extension (GNOME requires a prompt for installation of extensions for security purposes).
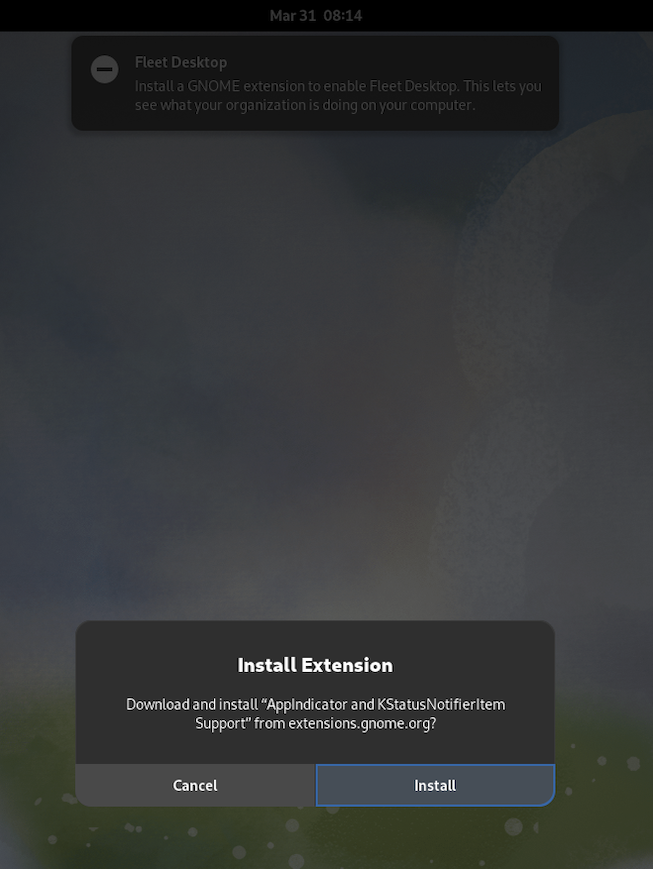

If the end-user hits
Cancelinstead ofInstallthen the extension won't be installed and the policy will continue to fail on the host. Fleet only deploys the script on the first failure of the policy, so the end-user won't be prompted again and again, just once. Admins can still run the script on such hosts manually.
Menu bar
After the extension is installed your users will see the Fleet icon on their menu bar: