Converting unix timestamps with osquery
{{articleSubtitle}}
Mike Thomas
Converting unix timestamps with osquery
{{articleSubtitle}}
Mike Thomas
Converting unix timestamps with osquery
Human readable timestamps
 Unix timestamps can be confusing for even the smartest Time Lord.
Unix timestamps can be confusing for even the smartest Time Lord.
If you are anything like me, and unix timestamps leave you thinking about the mysterious numbers in Lost, you’re going to want to convert them into something more human friendly. Running your timestamp through any number of online converters is one way to go, but it’s a clunky process.
 Hmm… 10800? That’s Thursday, January 1, 1970 3:00:00 AM, if I’m not mistaken.
Hmm… 10800? That’s Thursday, January 1, 1970 3:00:00 AM, if I’m not mistaken.
Thankfully, we can easily convert unix timestamps directly in osquery:
SELECT
unixtime,
datetime(unixtime, 'unixepoch') AS timestamp
FROM
(SELECT 1623366772 AS unixtime);
unixtime = 1623366772
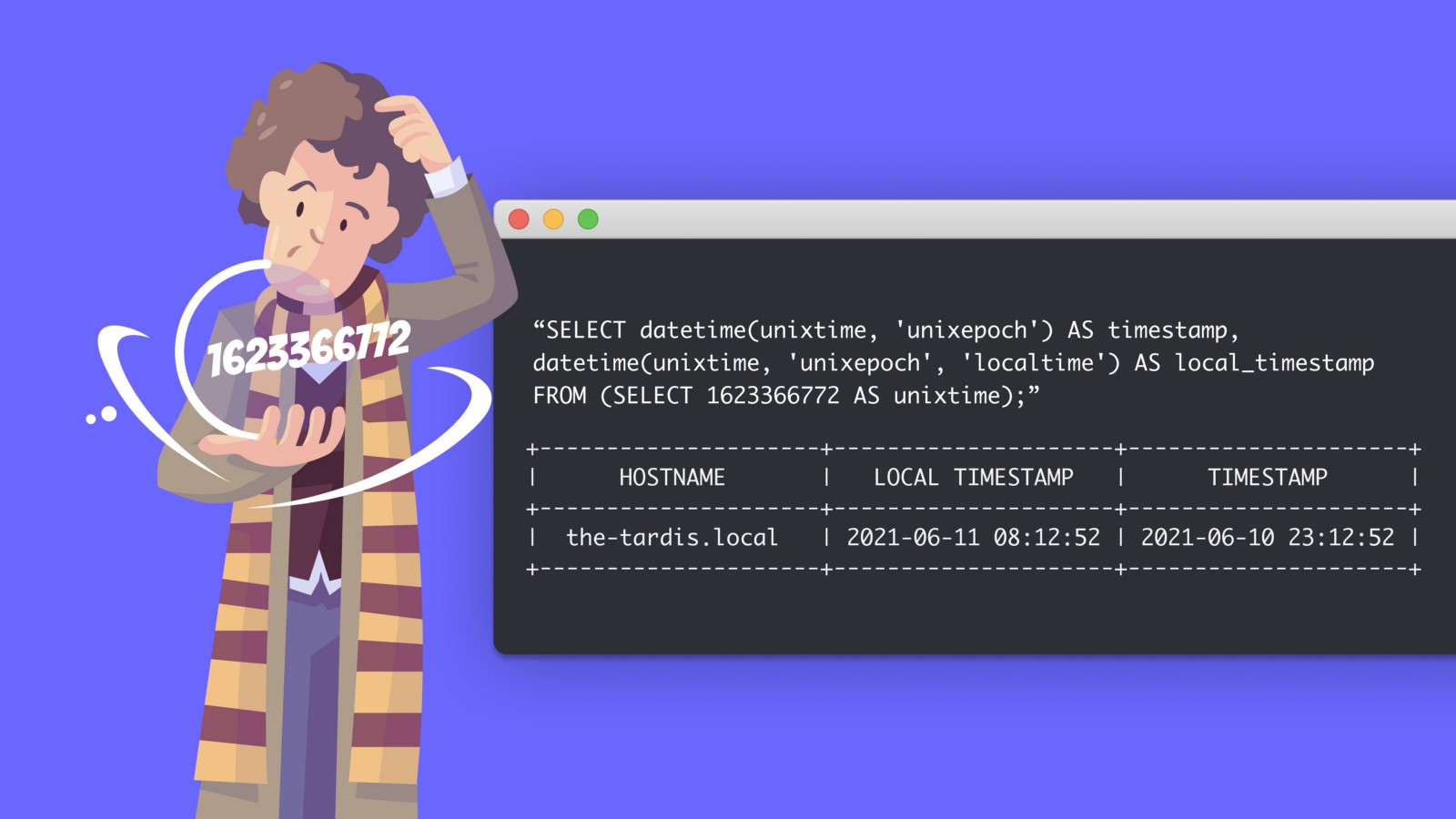
timestamp = 2021-06-10 23:12:52The above query returns the time in UTC, but what if we want to get the local timestamp for the system being queried?
SELECT
datetime(unixtime, 'unixepoch') AS timestamp,
datetime(unixtime, 'unixepoch', 'localtime') AS local_timestamp FROM
(SELECT 1623366772 AS unixtime);
timestamp = 2021-06-10 23:12:52
local_timestamp = 2021-06-11 8:12:52We can take this further by baking this idea into any of our queries. Let’s run a simple query to get all running processes on our host.
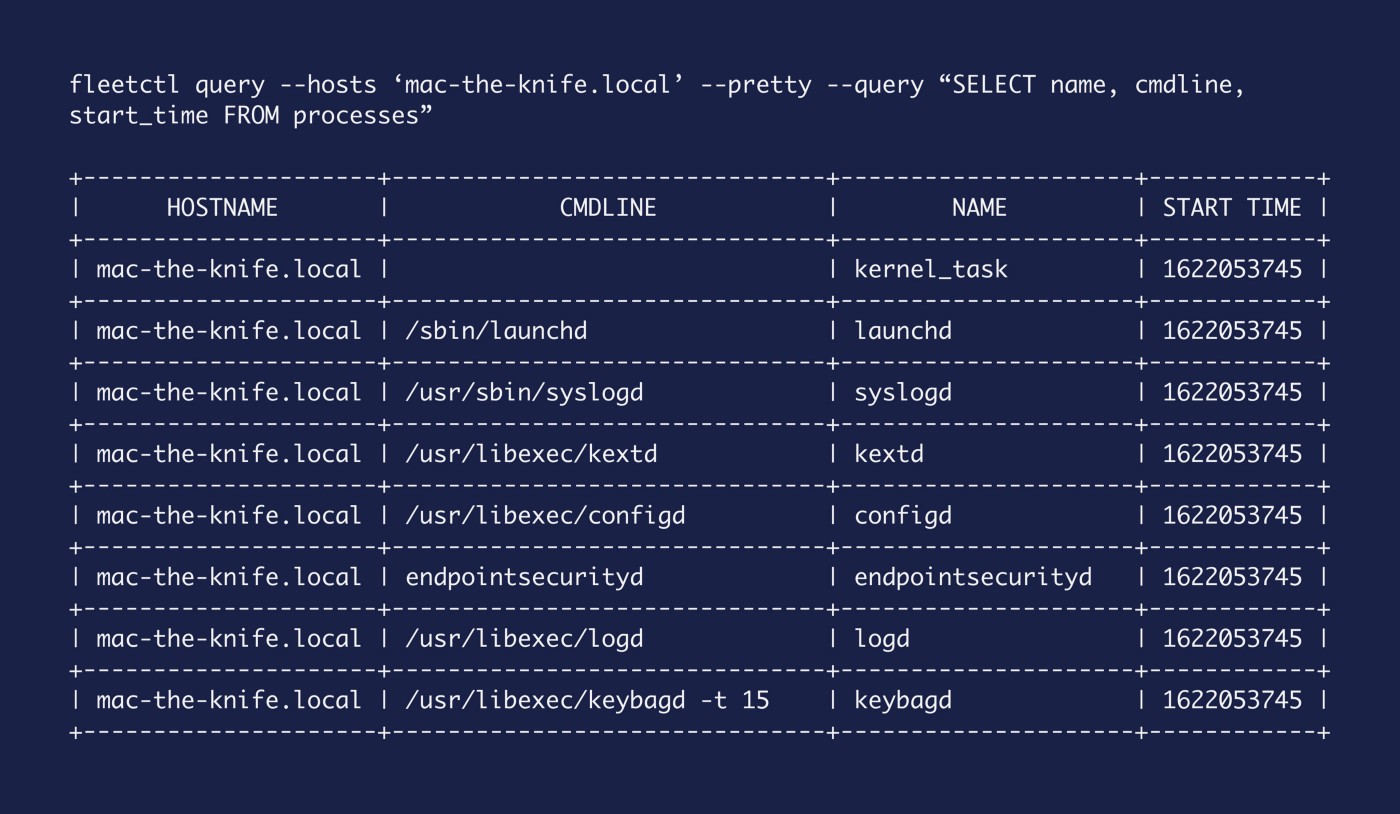
SELECT
name, cmdline, start_time
FROM
processesAs you can see, we have start_time listed in unix time again.
So let’s augment our query with the datetime line from before to give us a more human friendly output for start_time.
SELECT
name, cmdline,
datetime(start_time, 'unixepoch') AS start_time
FROM
processes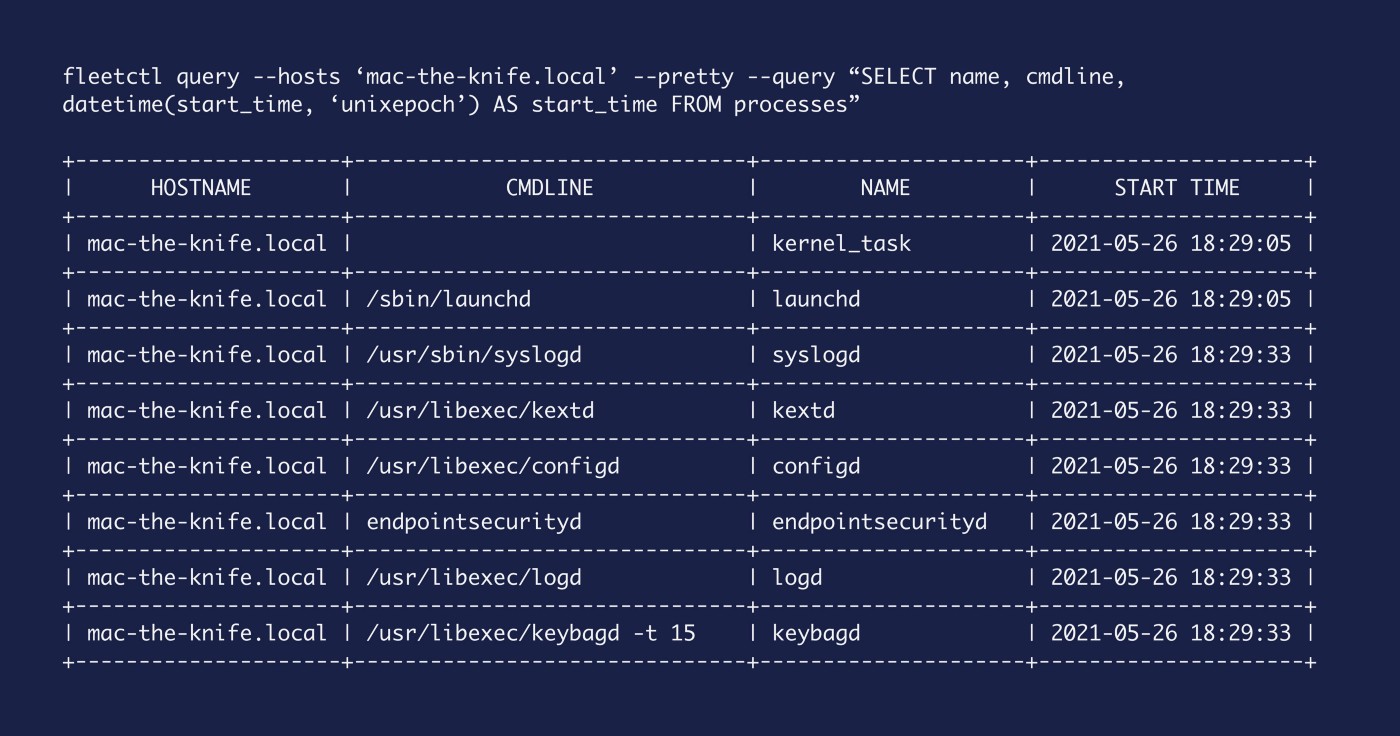
And finally, as before, we can of course output that data as the local time for our host by you guessed it, adding localtime to our query.
SELECT
name, cmdline,
datetime(start_time, 'unixepoch', 'localtime') AS start_time
FROM
processes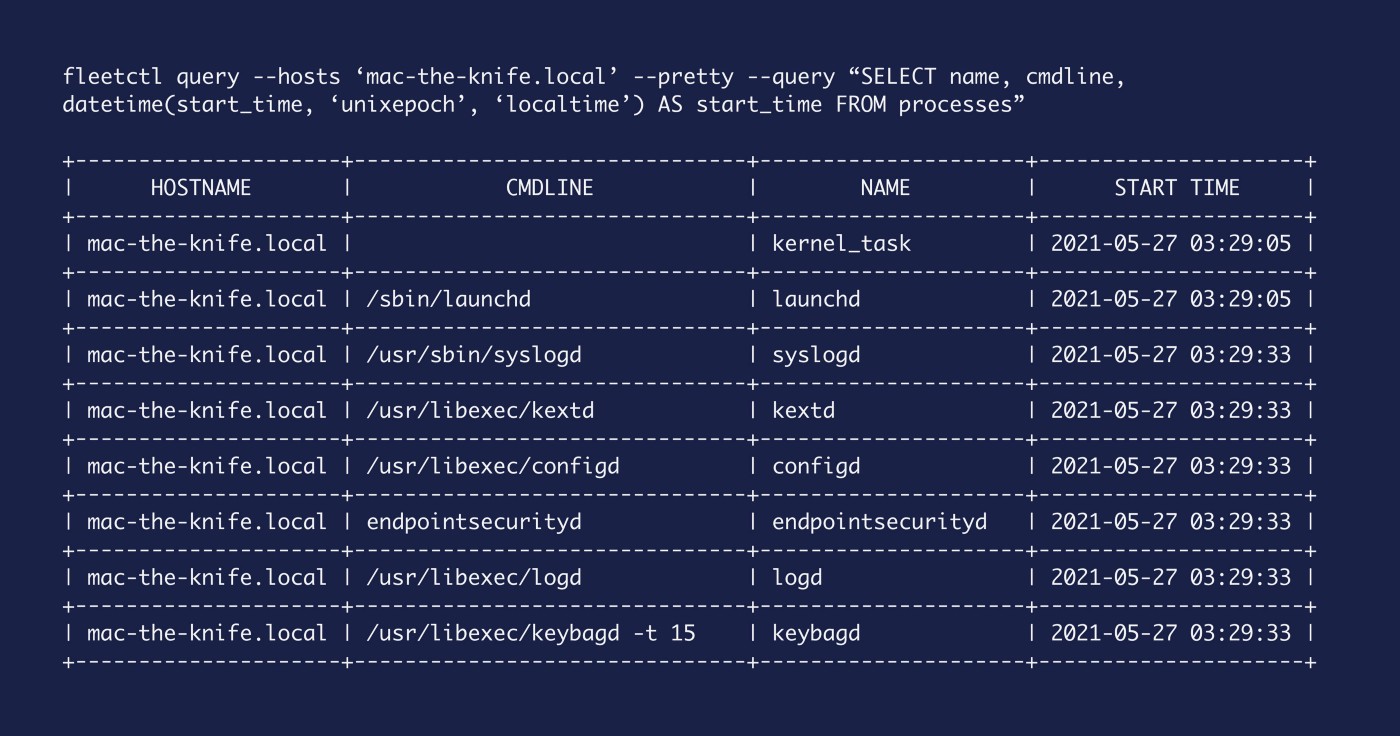
So there we go. Simple, human readable timestamps with osquery.
Could this post be more helpful?
Let us know if you can think of any other example scenarios you’d like us to cover.